- 链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/f23604257af94d939848729b1a5cda08
难点 #
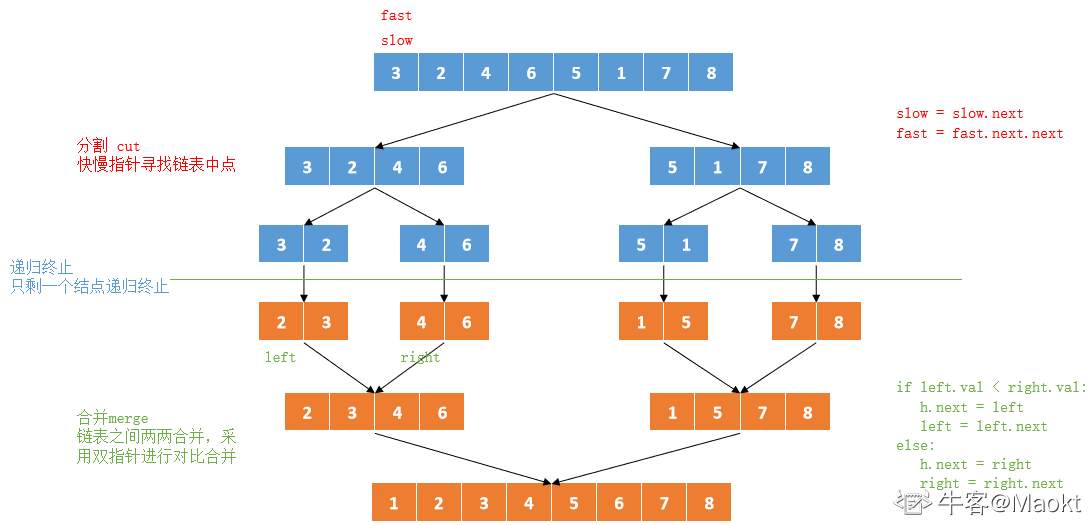
主要通过递归实现链表归并排序,有以下两个环节:
- 分割 cut 环节:
- 找到当前链表中点,并从中点将链表断开(以便在下次递归 cut 时,链表片段拥有正确边界);
- 使用 fast,slow 快慢双指针法,奇数个节点找到中点,偶数个节点找到中心左边的节点。
- 找到中点 slow 后,执行 slow.next = None 将链表切断。
- 递归分割时,输入当前链表左端点 head 和中心节点 slow 的下一个节点 tmp(因为链表是从 slow 切断的)。
- cut 递归终止条件: 当head.next == None时,说明只有一个节点了,直接返回此节点
- 合并 merge 环节: 将两个排序链表合并,转化为一个排序链表。
- 双指针法合并,建立辅助ListNode h 作为头部。
- 设置两指针 left, right 分别指向两链表头部,比较两指针处节点值大小,由小到大加入合并链表头部,指针交替前进,直至添加完两个链表。
- 返回辅助ListNode h 作为头部的下个节点 h.next。
- 时间复杂度 O(l + r),l, r 分别代表两个链表长度。
- 特殊情况,当题目输入的 head == None 时,直接返回None。
图解:
代码 #
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param head ListNode类 the head node
* @return ListNode类
*/
public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) {
// write code here
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
// 使用快慢指针寻找链表的中点
ListNode fast = head.next, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
ListNode tmp = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
// 递归左右两边进行排序
ListNode left = sortInList(head);
ListNode right = sortInList(tmp);
// 创建新的链表
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = h;
// 合并 left right两个链表
while (left != null && right != null) {
// left right链表循环对比
if (left.val < right.val) {
h.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
h.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
h = h.next;
}
// 最后添加未对比的链表部分判断左链表是否为空
h.next = left != null ? left : right;
return res.next;
}
}
